dna arror directionality
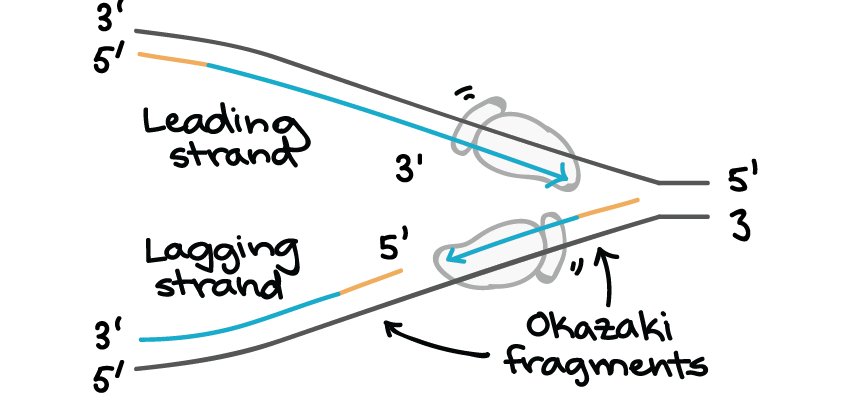
The Okazaki fragments each require a primer made of RNA to start the synthesis. Use arrows to show the direction of synthesis for the new DNA strands.
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
Along the leading strand DNA primase only needs to synthesise an RNA primer once at the beginning to initiate DNA polymerase.

. Directionality of DNA replication fork movement strongly affects the generation of spontaneous mutations in Escherichia coli J Mol Biol. As you can see in when the two parent strands of DNA are separated to begin replication one strand is oriented in the 5 to 3 direction while the other strand is oriented in the 3 to 5 direction. The side of the chain on the left begins with a free phosphate group at the top and ends with a.
A replication bubble is shown below. One gene is on one strand of the DNA and a gene in the opposite direction would be on the other strand. If you think about it each cell contains all of the DNA you need to make the other cells.
The arrow indicates the orientation of the T-DNA insert within the chromosome. Notice that in the two figures above the two strands of a DNA molecule are antiparallel that is they run in different directions. Affiliation 1 Department of.
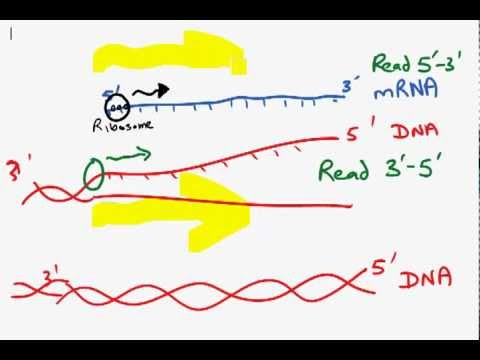
One of the template strands is read in a 3 to 5 direction therefore the new strand will be formed in a 5 to 3 direction. New DNA can elongate only in the 5 3 direction. Direction of transcription proceeds towards the translation proceeds of the longest RNA transcript.
DNA replication however is inflexible. One strand of DNA is in the 5 3 direction and while the other strand of DNA is in the 3 5 direction View the full answer. DNA is a template for RNA so the arrow between then is representative of base-pairing with thymine being substituted with Uracil to create RNA.
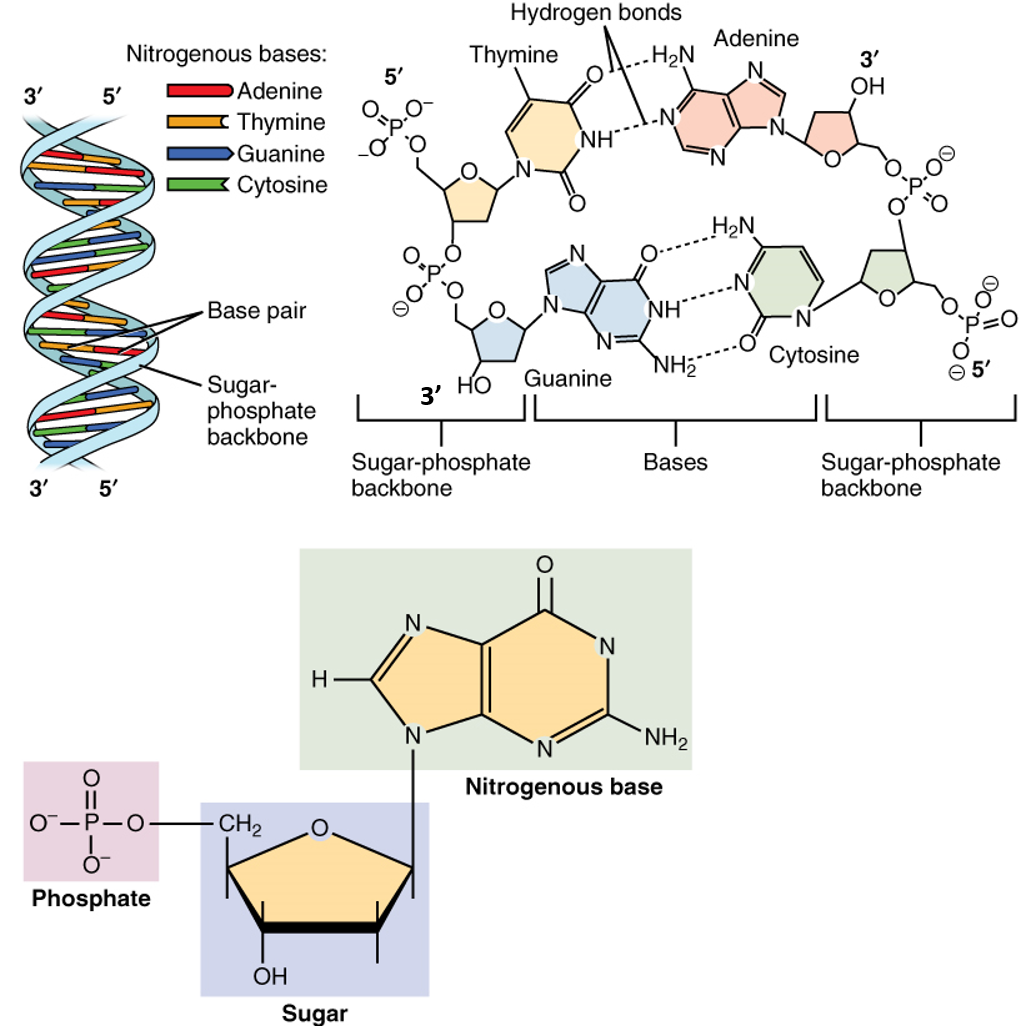
Both strands run antiparallel to each other meaning one strand is. They are not identical however they compliment each other. Shortly after DNA replication has begun you find two.
Up The sequence 5-TACGGATCTGGATCCT-3 is part of a gene that encodes. Draw and label the RNA primers and the new DNA strands that have been synthesized. The genes in DNA encode protein molecules.
As far as the cell is concerned there is no difference and there is no directionality. What the arrow could mean is a specific strand of DNA that is used in RNA. We look at DNA running from 5 to 3 or 3 to 5 when referring to the direction of DNA.
The open reading frame ORF of a gene is therefore usually represented as an arrow indicating the direction in which the sense strand is read. The proposal follows a recent incident out of San Francisco in which the police department using DNA from a 2016 rape kit linked the DNA of. Transcription stops at the end of the Transcription Terminator shown in blue.
Authors K Yoshiyama 1 K Higuchi H Matsumura H Maki. The Genes from DNA is what defines the structure of RNA. Below is the double-stranded DNA sequence of part of a hypothetical yeast genome which happens to contain a very small gene.
And we start out from a single cell and we end up with trillions of cells. Answer- According to the given question- The DNA is a double-helix structure where both the DNA strands are antiparallel to each other ie. First the ribosome moves along the mRNA in the 5-to-3direction which requires the elongation factor G in a process called translocation.
From the electron micrograph above the arrow indicates the DNA strand. The enzyme that carries out the replication DNA polymerase only functions in the 5 to 3 direction. In Figure 8-5 draw the one gene at much higher resolution with the following components.
Here we show that this machine operates unidirectionally with respect to the chromosome of Escherichia coli. The arrow point in the 5 to 3 direction beginning with the left border DNA. In DNA Adenine A always pairs with thymine T and guanine G always pairs with cytosine C.
This newly formed strand is referred to as the leading strand. Only certain bases can pair together to form base pairs. And direction of a 3.
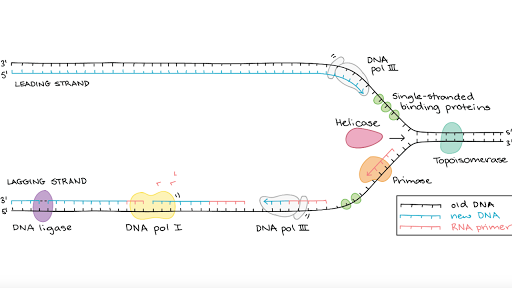
DNA mismatch repair MMR is critical to avoid mutations that can lead to genetic disease cancer and death. Since the two strands of a DNA double helix are antiparallel this 5-to-3 DNA synthesis can take place continuously on only one of the strands at a replication fork the leading strand. Polymerization of DNA for both the lagging and the leading strands is in the 5 to 3 direction.
Inverted and opposite to the other. Label the leading and lagging strands. The DNA polymerase enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of new DNA by adding nucleotides to a preexisting chain.
Assume that DNA replication is occurring in this area but RNA primers have not yet been removed. And during that process of cell division all of the information in a cell has to be copied and it has to. DNA replication is probably one of the most amazing tricks that DNA does.
This is because DNA polymerase is able to extend the. DNA consists of two strands. This sense or coding strand runs in the 5 to 3 direction where the numbers refer to the carbon atoms of the backbones ribose sugar.
Of the template. The MMR system is evolutionarily conserved from bacteria to humans and is an example of a remarkable molecular machine. DNA RNA polymerases RNAs.
The two genes are transcribed from opposite DNA strands which are antiparallel so the genes must be transcribed in opposite directions to maintain the 5 to 3 direction of transcription. Because DNA polymerase can only synthesize DNA in a 5 to 3 direction the other new strand is put together in short pieces called Okazaki fragments. The DNA strand that is made continuously is referred to as the leading strand.
A self-correcting DNA polymerase enzyme catalyzes nucleotide polymerization in a 5-to-3 direction copying a DNA template strand with remarkable fidelity. Transcription starts at the Transcription Start Site TSS after the promoter shown in yellow and proceeds in the direction of the arrow.

Why Can T Dna Polymerase Attach Things To The 5 End Of A Strand Of Dna

Chromosomal Directionality Of Dna Mismatch Repair In Escherichia Coli Pnas

Dna Function Structure With Diagram Article Khan Academy

Directionality Molecular Biology Wikiwand

Semidiscontinuous Dna Replication Youtube
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
Chapter 4 Dna Rna And The Human Genome Chemistry

Chapter 6 Dna Repair And Replication Flashcards Quizlet

Leading And Lagging Strands In Dna Replication Video Khan Academy
Dna And Protein Synthesis Direction 3 Or 5 Mp4 Youtube

Directionality Molecular Biology Wikiwand

High Accuracy Lagging Strand Dna Replication Mediated By Dna Polymerase Dissociation Pnas
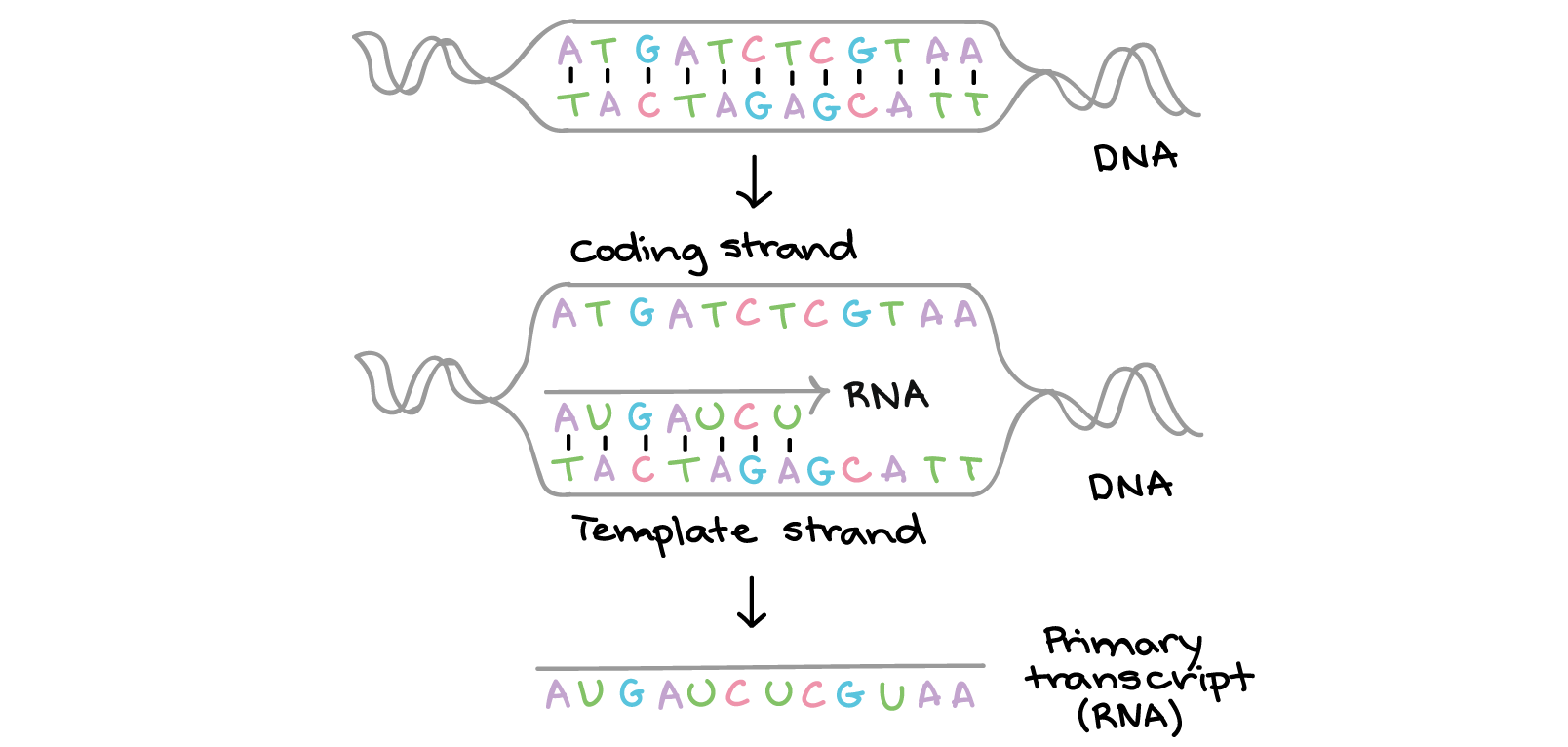
Intro To Gene Expression Central Dogma Article Khan Academy

Persistence Of Rna Transcription During Dna Replication Delays Duplication Of Transcription Start Sites Until G2 M Sciencedirect
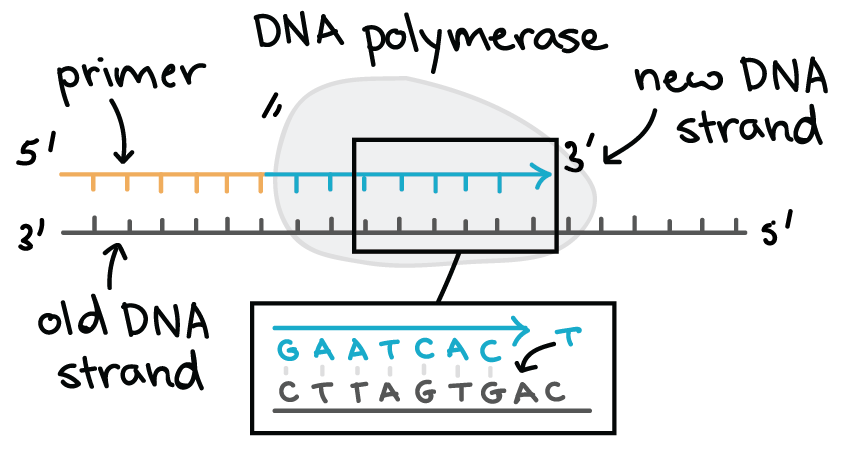
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy
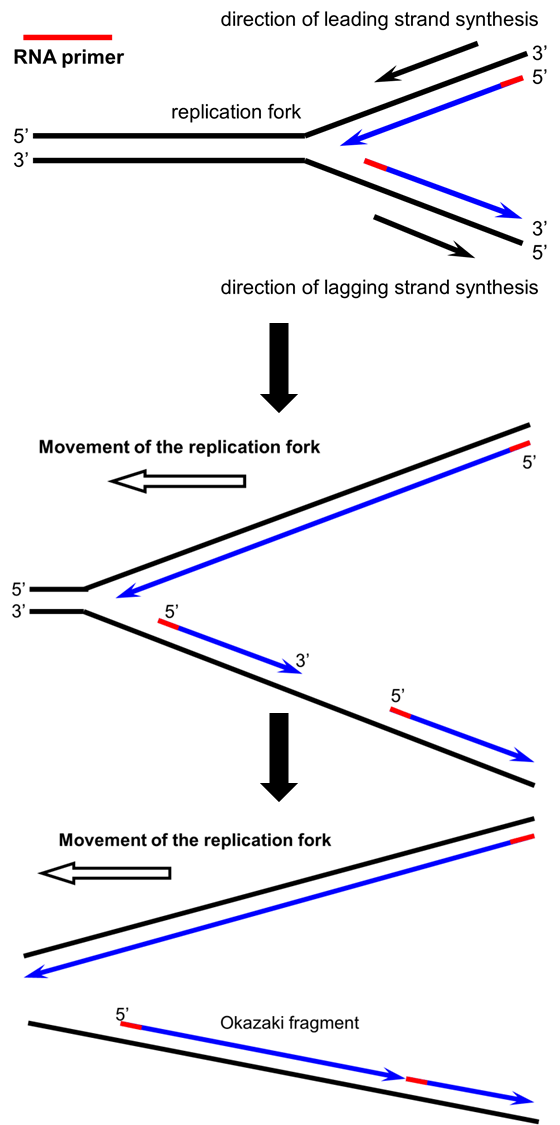

Comments
Post a Comment